When you’re deploying large language models in your enterprise, you’re not just handling AI; you’re processing data that could make or break your compliance posture. The reality is stark:
LLM prompts and outputs often contain personal data, making them subject to GDPR principles such as lawfulness, minimization, and storage limitation. This includes personal data as defined by GDPR, governed by the principles outlined in Article 5.
Meanwhile, SOC 2 Trust Services Criteria demand security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy controls across your entire LLM stack.
Think of it like this: your LLM isn’t just a clever chatbot, it’s a data processing engine that regulators are watching closely. The EU AI Act’s phased timeline is already in motion, with obligations rolling out through 2025 and beyond. (AI Act implementation timeline).
CISOs and DPOs who get ahead of this curve aren’t just checking compliance boxes; they’re building competitive advantages.
What Does “Secure & Compliant LLM” Actually Mean?
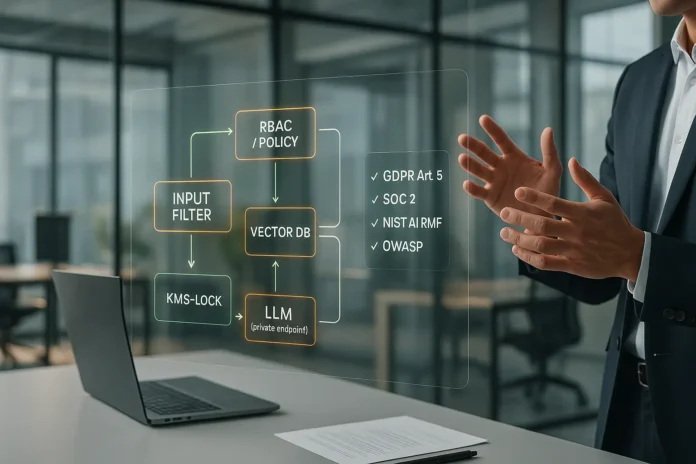
A secure LLM deployment treats every prompt, output, log entry, and embedding as potential personal data processing under GDPR.
This means applying data minimisation before retrieval, ensuring a lawful basis for processing, and maintaining integrity and confidentiality throughout the AI lifecycle.
Your audit lens should cover SOC 2’s five Trust Services Criteria while using NIST AI RMF’s Govern-Map-Measure-Manage framework as your risk backbone.(NIST AI Risk Management Framework (GM³)).
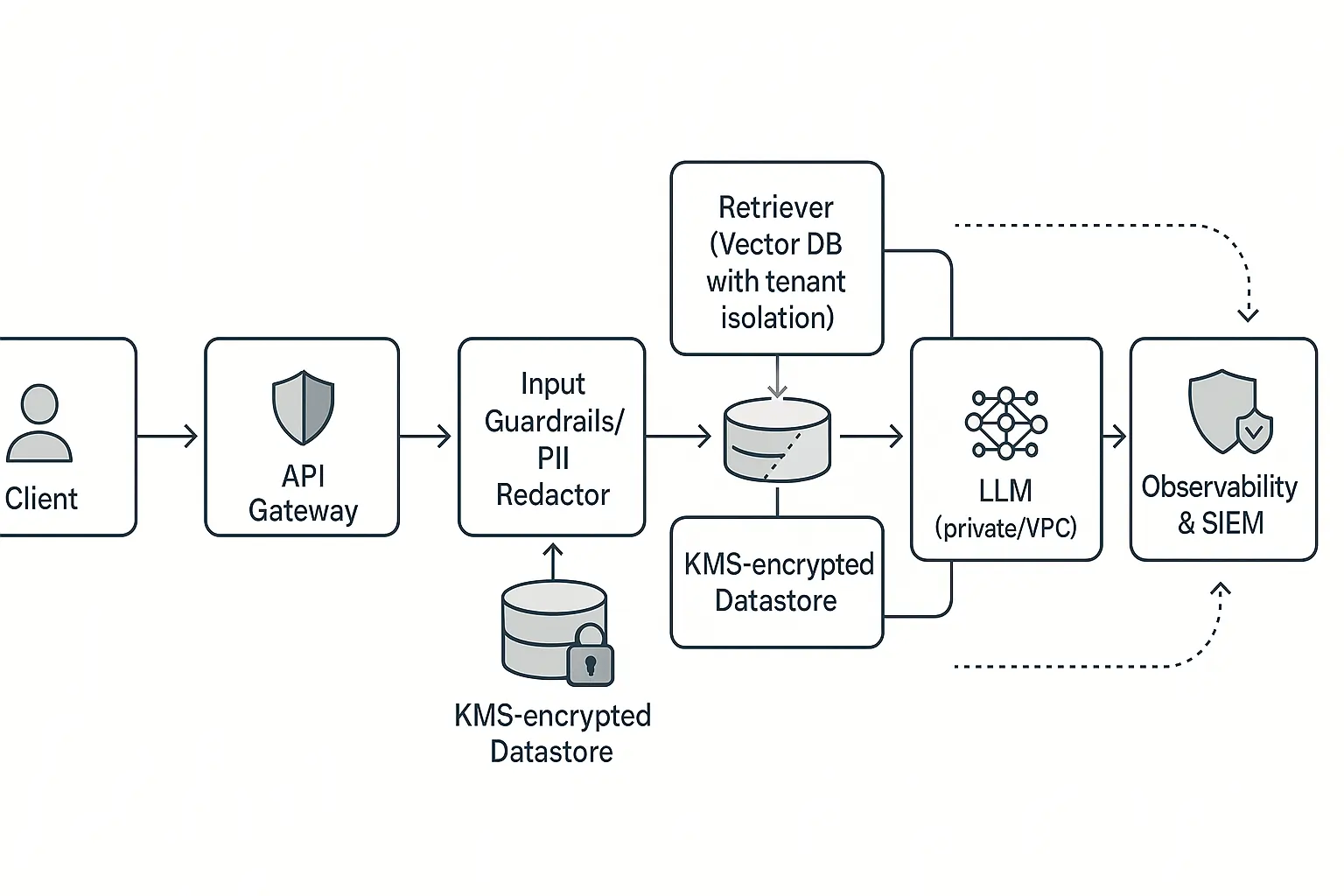
The enterprise LLM integration overview becomes critical here because you need visibility into every data flow. Most organisations discover they’re processing personal data in ways they never anticipated, such as chat logs, embeddings, and even model fine-tuning datasets, which can contain PII.
Why This Matters Now
The EU AI Act timeline is no longer theoretical. With obligations phasing in throughout 2025, general-purpose AI model providers face increasing scrutiny. Even if you’re US-based, cross-border data flows and multinational operations mean these regulations affect your LLM deployments.(AI Act implementation timeline (European Parliament Think Tank)).
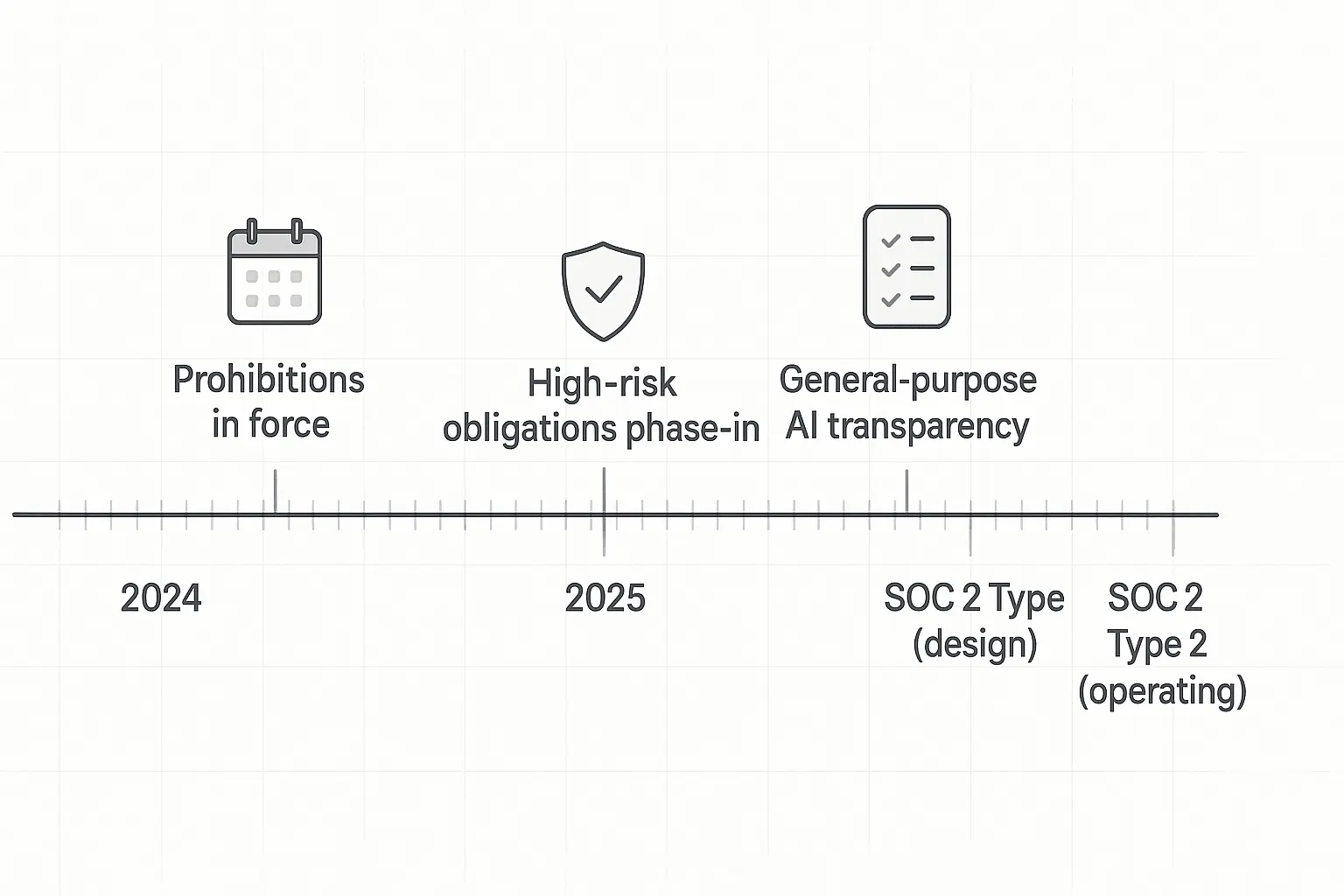
Innovative security teams are using this regulatory pressure as leverage to secure budget for proper AI governance infrastructure. It’s easier to get executive buy-in when you can point to specific compliance deadlines.
Which Risks Are Unique to LLMs and How Do We Mitigate Them?
LLMs introduce attack vectors that traditional security frameworks barely address. OWASP’s Top 10 for LLM Applications catalogues threats like prompt injection, data leakage(OWASP Top-10 for Large Language Model Applications), model poisoning, and insecure plugins that can bypass conventional security measures.
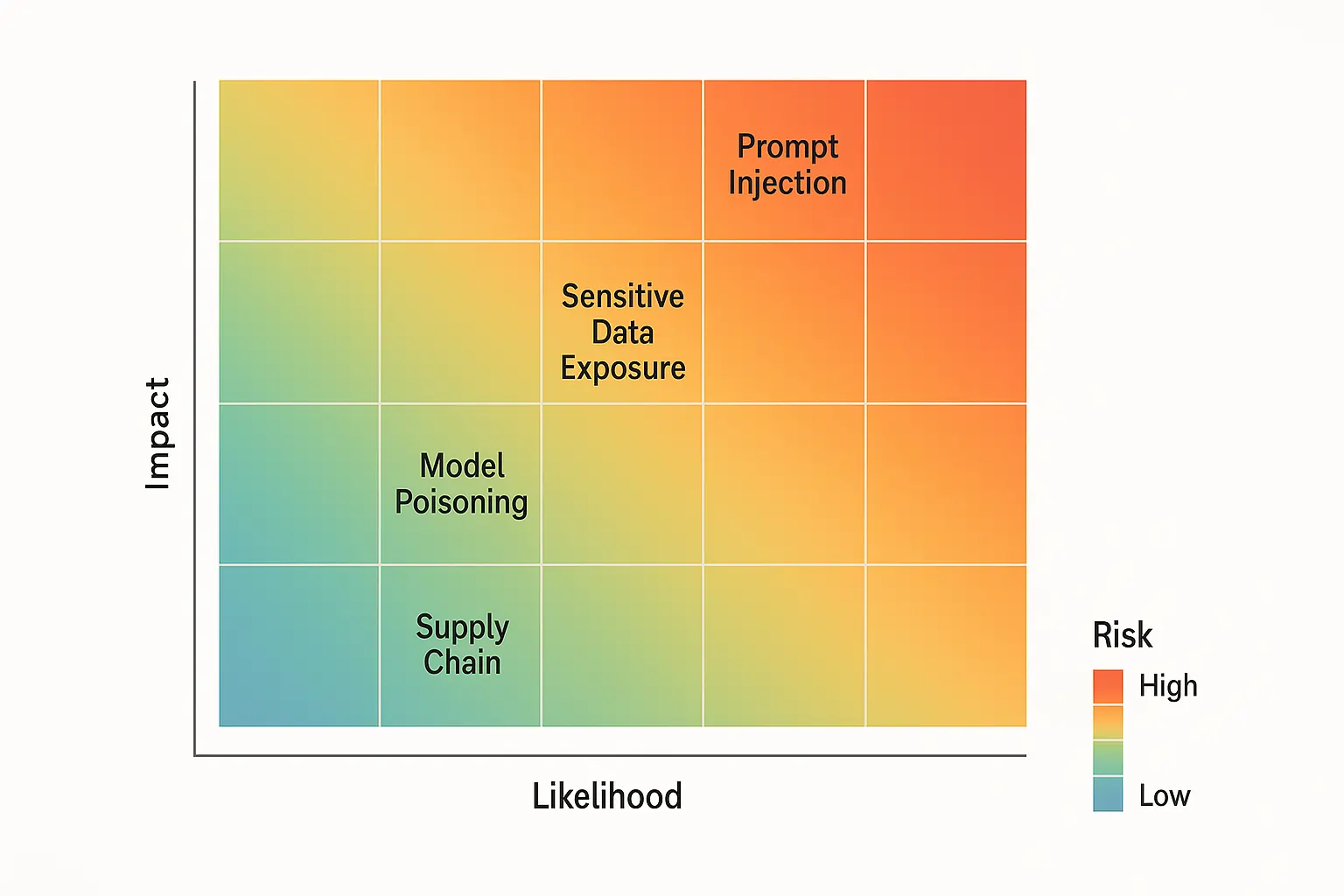
Prompt injection attacks manipulate model behaviour to exfiltrate data, while indirect prompt injection can abuse multimodal inputs to trigger unauthorised actions.
Here’s your essential control framework:
Input/Output Guardrails: Deploy real-time prompt filtering and output scanning without killing performance. Modern solutions can process requests in under 50ms while blocking injection attempts and PII leakage.
RBAC + Least Privilege: Lock down access to prompts, outputs, and embeddings. Your developers shouldn’t have the same LLM permissions as your customer support team.
PII Redaction & Minimisation: Scrub sensitive data before it hits your vector databases or training pipelines. This satisfies GDPR minimisation while reducing your attack surface.
KMS-backed Encryption: Use separate keys per tenant and region. HSM separation of duties isn’t optional when you’re processing regulated data at scale.
Monitoring & Evaluations: Implement red-team testing and regression gates. The RAG security best practices guide covers tenant-safe patterns that prevent cross-contamination.
Stats That Matter for Your Risk Register
GDPR Article 5 principles provide your policy framework for lawfulness, minimisation, storage limits, and integrity requirements. SOC 2’s five criteria become your acceptance criteria headings in security tickets. NIST AI RMF, combined with the Generative AI Profile, provides a standardised risk workflow that auditors recognise.
Recent research from Cisco Talos found hundreds of exposed LLM servers online, highlighting how quickly AI infrastructure can become an attack vector. Meanwhile, IBM’s prompt injection research shows these attacks work across major model providers, not just experimental setups.
How Do We Implement Controls That Satisfy GDPR & SOC 2 Without Killing Velocity?
The key is to build compliance into your development workflow, rather than bolting it on afterwards. NIST AI RMF provides a practical four-step approach that maps directly to DevOps practices most teams already understand.
Govern: Assign clear ownership for LLM data flows. Define your data classes, prompts, outputs, logs, and embeddings and establish retention policies with documented lawful basis. This isn’t just a privacy exercise; it’s operational clarity that reduces security incidents.
Map: Inventory your data flows from ingest through retrieval, inference, and egress. Tag PII at every stage and document cross-border transfers. The secure setup checklist provides templates for this mapping exercise.
Measure: Run OWASP LLM evaluations against injection and leakage scenarios. Set pass/fail gates before production deployment. Track residual risk and make it visible to business stakeholders.
Manage: Roll out RBAC, encryption, and logging with automated DPIA triggers for model or version changes. Your CI/CD pipeline should block deployments that don’t meet your risk thresholds.
Framework Comparison for Auditor Evidence
| Framework | Coverage | Required Evidence | Application Scope |
|---|---|---|---|
| GDPR | Data principles, rights, retention | DPIA, DPA agreements, data maps, DSAR exports | All personal data processing in prompts/outputs/logs |
| SOC 2 | Trust Services Criteria | Access logs, change controls, KMS configs, incident runbooks | Service organisation controls across the LLM stack |
| NIST AI RMF | Risk lifecycle (GM³) | Risk registers, evaluation reports, red-team results | Model and system risk governance |
| OWASP LLM Top 10 | Threat catalog | Test cases, guardrail configurations, break-glass procedures | Application-level secure design and evaluations |
The imaginative play utilises NIST AI RMF for risk governance, generating evidence that naturally aligns with SOC 2 audits. This avoids duplicate work while satisfying multiple compliance requirements.
How Do We Keep Tenant Data Safe in RAG and Real-Time Apps?
Multi-tenant LLM deployments are where most organisations expose themselves to data leakage risks. Your RAG blueprint requires several key components, including per-tenant vector stores, context redaction, tool allow-lists, egress controls, and regional KMS keys. Each pattern maps to specific SOC 2 criteria and GDPR transfer requirements.(Pinecone multitenancy with namespaces).
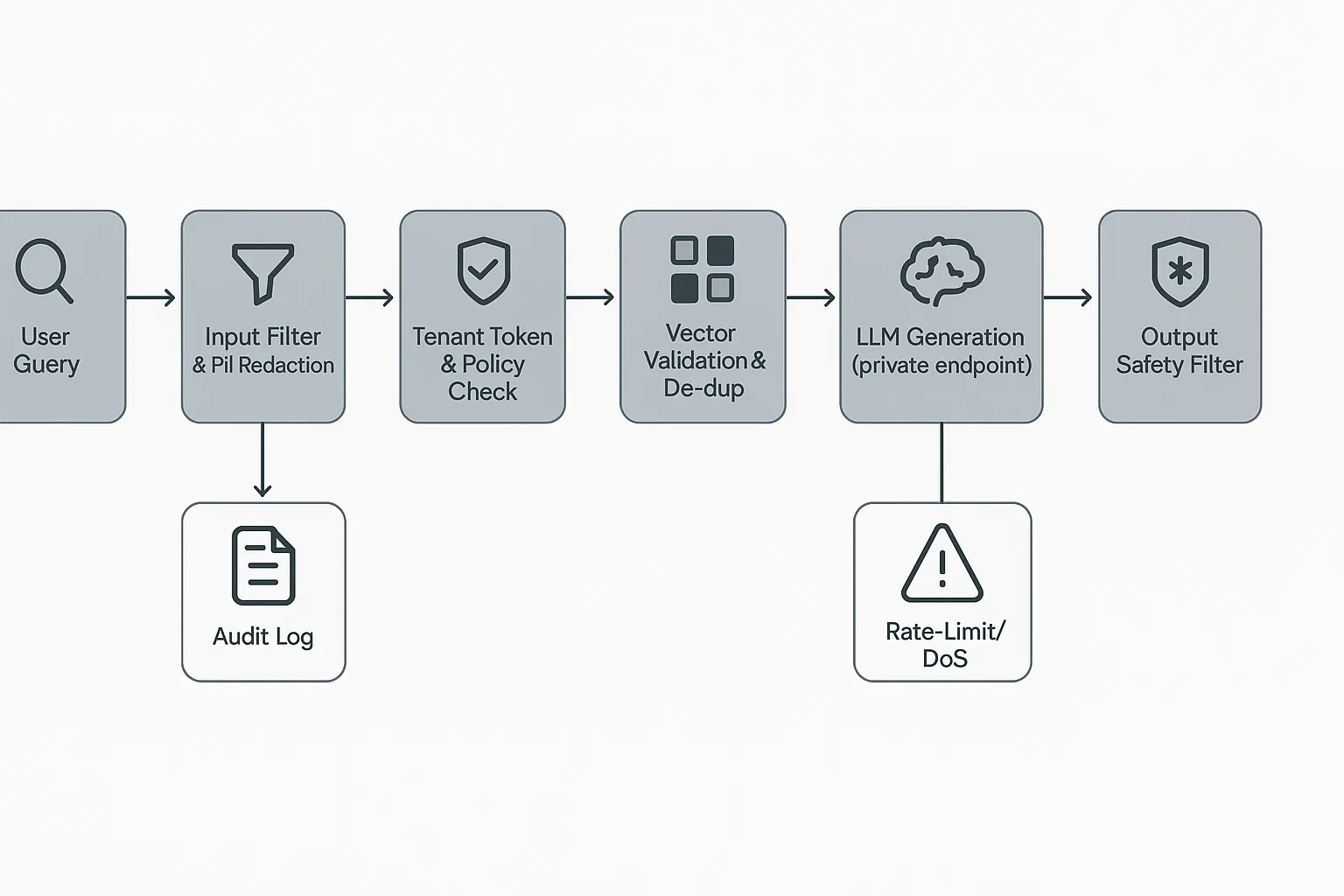
Real-time guardrails present the most significant technical challenge. You need lightweight I/O filters, cache-first retrieval, batched logging, and async PII scrubbing, all while maintaining sub-100ms response times.
The security certifications & integration tools resource covers vendor solutions that can handle this complexity.
The tenant-safe approach isn’t just about compliance; it’s about business continuity. Data breaches in multi-tenant environments can affect hundreds or thousands of customers simultaneously.
It’s better to over-engineer your isolation boundaries than to explain a cross-tenant data leak to regulators.
What Documents Do Auditors and DPAs Actually Ask For?
Most compliance teams underestimate the documentation burden for LLM audits. Your compliance pack should include DPIA templates specific to LLM processing, Article 30 records, DPA and sub-processor agreements, model cards with training data lineage, red-team evaluation reports, access and key management evidence, and incident postmortems.(ICO: when and how to do a DPIA)
Cross-reference each document to your applicable frameworks. Your GDPR DPIA should address NIST AI RMF risk categories.
Your SOC 2 evidence should demonstrate OWASP LLM threat mitigation. This interconnected approach demonstrates to auditors that you understand the regulatory landscape holistically.
The organisations that sail through audits are those that treat documentation as a byproduct of good operational practices, not a separate compliance exercise.
What Should We Prioritise This Quarter?
Q1: Complete your data mapping and DPIA. Implement PII blocking for prompts and outputs. This foundation work enables everything else.
Q2: Deploy RBAC and per-tenant KMS. Establish logging and retention policies with automated enforcement.
Q3: Run OWASP-style evaluations and establish break-glass procedures. Review your supply chain dependencies for AI components.
Q4: Refresh SOC 2 evidence collection and update AI Act readiness based on final implementation guidance.
This phased approach balances regulatory deadlines with operational reality. Most teams can’t implement everything simultaneously without disrupting business operations.
FAQ
Q: Do prompts and outputs count as personal data?
A: Yes, treat them as data processing and apply minimisation and retention controls under GDPR.
Q: What’s the difference between SOC 2 Type 1 and Type 2?
A: Type 1 audits design effectiveness; Type 2 audits operating effectiveness over time.
Q: Which framework comes first, NIST or SOC 2?
A: Use NIST AI RMF for risk governance; evidence flows into SOC 2 audits naturally.
Q: How do we test for prompt injection?
A: Adopt OWASP LLM Top-10 test cases in your pre-production gates and CI/CD pipeline.
The reality of LLM security isn’t about choosing between innovation and compliance; it’s about building systems that enable both. Organisations that nail this balance will outperform competitors still struggling with basic AI governance. Your move.